Introduction
Iron deficiency and anemia are common health problems worldwide, especially in developing countries, pregnant women, children and women of childbearing age. Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) not only affects the physical and cognitive function of individuals, but may also increase the risk of pregnancy complications and developmental delay in children. Therefore, early screening and intervention are essential. Among the many detection indicators, ferritin has become an important tool for screening iron deficiency and anemia due to its high sensitivity and specificity. This article will discuss the biological characteristics of ferritin, its advantages in the diagnosis of iron deficiency and anemia, and its clinical application value.
Biological Characteristics of Ferritin
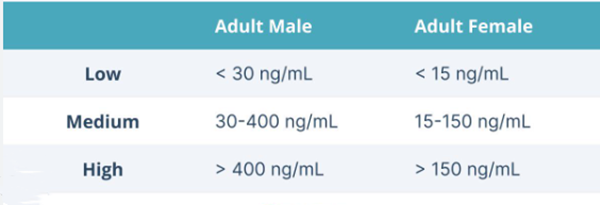
Ferritin is an iron storage protein widely present in human tissues. It is mainly synthesized by the liver, spleen and bone marrow. Its core function is to store iron and regulate the balance of iron metabolism. In the blood, the concentration of ferritin is positively correlated with the body’s iron reserves. Therefore, serum ferritin levels are one of the most sensitive indicators of the body’s iron storage status. Under normal circumstances, the ferritin level in adult males is about 30-400 ng/mL, and in females it is 15-150 ng/mL, but in the case of iron deficiency, this value will be significantly reduced.
Advantages of Ferritin in Iron Deficiency Screening
1. High sensitivity, early detection of iron deficiency
The development of iron deficiency is divided into three stages:
- Iron deficiency stage: storage iron (ferritin) decreases, but hemoglobin is normal;
- Iron deficiency erythropoiesis stage: ferritin further decreases, transferrin saturation decreases;
- Iron deficiency anemia stage: hemoglobin decreases, and typical anemia symptoms appear.
Traditional screening methods (such as hemoglobin testing) can only detect problems in the anemia stage, while ferritin testing can detect abnormalities in the early stage of iron deficiency, thus providing an opportunity for early intervention.
2. High Specificity, Reducing Misdiagnosis
Many diseases (such as chronic inflammation and infection) can cause anemia, but they are not caused by iron deficiency. In this case, relying solely on hemoglobin or mean corpuscular volume (MCV) may misjudge the cause. Ferritin testing can accurately distinguish iron deficiency anemia from other types of anemia (such as anemia of chronic disease), improving diagnostic accuracy.
3. Fast and convenient, suitable for large-scale screening
Modern biochemical testing technology makes ferritin determination faster and more economical, and is suitable for public health projects such as community screening, maternal and infant health care, and child nutrition monitoring. Compared with invasive tests such as bone marrow iron staining (gold standard), serum ferritin testing is easier to promote.
Clinical Applications of Ferritin in Anemia Management1. Guiding iron supplementation treatment
Ferritin levels can help doctors determine whether patients need iron supplementation and monitor the effectiveness of treatment. For example:
- Ferritin
- Ferritin
- When treatment is effective, ferritin levels will gradually rise and can be used to evaluate the efficacy
1. Guiding Iron Supplementation
Ferritin levels help clinicians determine the need for iron therapy and monitor treatment efficacy. For example:
- Ferritin
- Ferritin
- During treatment, rising ferritin levels confirm therapeutic effectiveness.
2. Screening of special populations
- Pregnant women: iron demand increases during pregnancy, and ferritin testing can prevent maternal and infant complications.
- Children: iron deficiency affects cognitive development, and early screening can improve prognosis.
- Patients with chronic diseases: such as patients with kidney disease and inflammatory bowel disease, ferritin combined with transferrin saturation can identify the type of anemia.
Limitations of Ferritin Testing and Solutions
Although ferritin is the preferred indicator for iron deficiency screening, it needs to be interpreted with caution in some cases:
- Inflammation or infection: Ferritin, as an acute phase reactant protein, may be falsely elevated in infection, tumor or chronic inflammation. In this case, it can be combined with C-reactive protein (CRP) or transferrin saturation for comprehensive judgment.
- Liver disease: Ferritin in patients with cirrhosis may increase due to liver cell damage and needs to be evaluated in combination with other iron metabolism indicators.
Conclusion
Ferritin testing has become an important tool for screening iron deficiency and anemia due to its high sensitivity, specificity and convenience. It can not only detect iron deficiency early and avoid the progression of anemia, but also guide precise treatment and improve patient prognosis. In public health and clinical practice, the promotion of ferritin testing can help reduce the disease burden of iron deficiency anemia, especially for high-risk groups (such as pregnant women, children and patients with chronic diseases). In the future, with the advancement of detection technology, ferritin may play a greater role in global anemia prevention and control.
We Baysen Medical is always focus on diagnostic technique to improve the quality of life . We have developed 5 technology platforms- Latex, colloidal gold, Fluorescence Immunochromatographic Assay, Molecular, Chemiluminescence Immunoassay, Our Ferritin test kit easy operation and can get test result in 15 mins.
Media Contact
Company Name: XIAMEN BAYSEN MEDICAL TECH CO., LTD.
Email: Send Email
Country: China
Website: https://www.baysenrapidtest.com/
